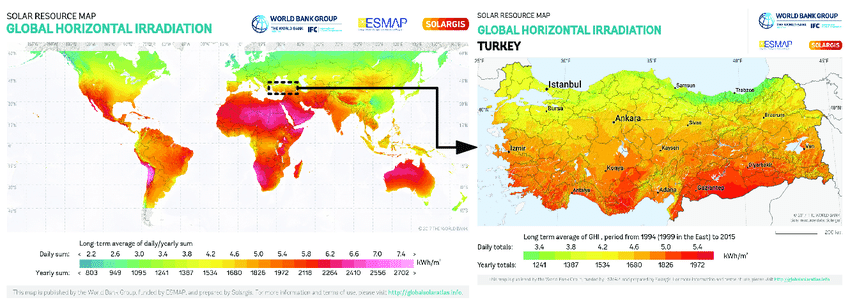
Global horizontal irradiance solar: Pros and Cons They Don’t Tell You
In the quest for sustainable energy solutions, Global Horizontal Irradiance solar (GHI) technology has emerged as a key contender. Yet, beneath its promising surface, lie nuances that often remain in the shadows. This article unveils the unspoken advantages and drawbacks of GHI solar, shedding light on the lesser-known aspects of this renewable energy source. Whether you’re an environmental advocate or a prospective solar adopter, understanding these nuances is crucial in the journey towards a greener future.
Pros of GHI Solar:
- Universality: GHI solar systems are highly versatile and can be deployed in a wide range of geographic locations. Unlike some solar technologies that require specific conditions like direct sunlight, GHI solar can generate power even on cloudy days, making it suitable for various climates.
- Energy Efficiency: GHI solar panels are known for their efficiency in converting sunlight into electricity. They can capture sunlight from multiple angles throughout the day, maximising energy production. This efficiency can make GHI solar a cost-effective choice in the long run.
- Reduced Environmental Impact: GHI solar systems produce clean, emissions-free energy, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution. They have a relatively low environmental footprint compared to fossil fuel-based power generation.
- Grid Independence: GHI solar installations can operate independently or in conjunction with the grid, offering energy security and flexibility. Excess energy can often be stored or sold back to the grid, providing a reliable source of income or backup power during grid outages.
- Minimal Space Requirements: GHI solar panels are typically ground-mounted and require less space compared to some other solar technologies. This makes them suitable for locations with limited available land or rooftop space.
Cons of GHI Solar:
- Intermittency: While GHI solar systems can generate power on cloudy days, their energy production is still dependent on sunlight. Nighttime and adverse weather conditions can disrupt energy generation, necessitating the use of energy storage solutions like batteries.
- Initial Cost: The upfront cost of GHI solar installations can be substantial, including the purchase of solar panels, inverters, and installation expenses. While prices have been decreasing, the initial investment remains a barrier for some.
- Aesthetic Concerns: Some individuals and communities have aesthetic concerns about the appearance of GHI solar installations, particularly in rural or scenic areas. Balancing the visual impact with the benefits of renewable energy can be a point of contention.
In conclusion, Global Horizontal Irradiance (GHI) solar has a compelling set of benefits and drawbacks. Its ability to generate energy in various conditions and its efficiency are significant advantages. However, intermittent energy generation, initial costs, land use considerations, and aesthetic concerns should also be weighed when considering GHI solar as an energy solution. Ultimately, understanding these pros and cons is essential for making informed decisions about adopting GHI solar technology.







