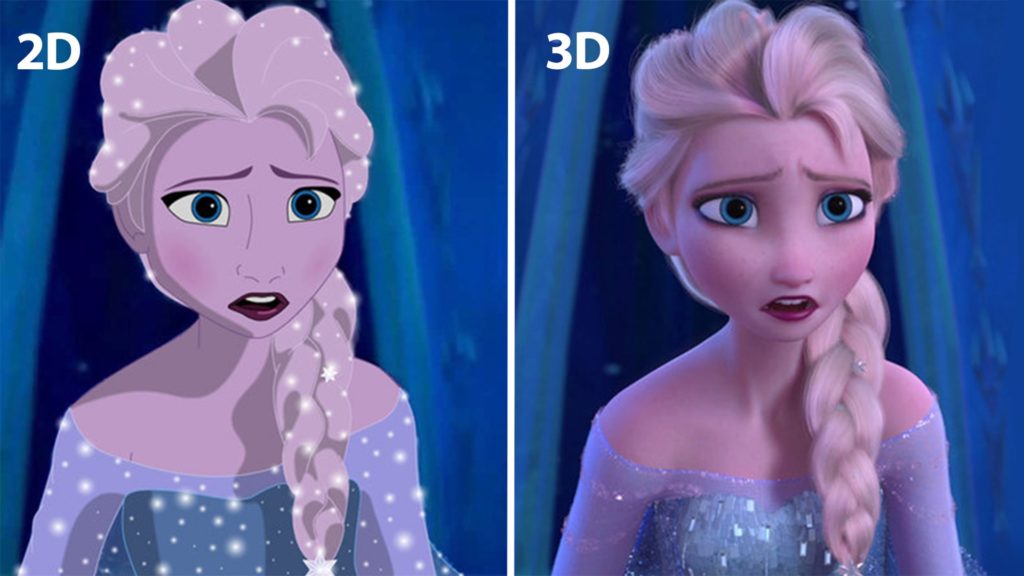

Difference of 2D and 3D Art
In the realm of game art and design, two primary forms of representation dominate the scene: 2D and 3D art.
Both forms have unique characteristics, applications, and require different skill sets from artists.
This article aims to clarify the differences between 2D art and 3D art, providing a deeper understanding of these two fundamental aspects of visual representation.

Understanding 2D Game Art
2D, or two-dimensional game art, exists on a flat surface and is defined by two dimensions: length and width.
This form of art includes drawings, paintings, sketches, and even digital art created on a computer.
2D art is often referred to as “flat” due to its nature of existing on a flat surface, such as a piece of paper or a computer screen. It does not have volume or depth.
Examples of 2D structures include sheets, circular objects, rectangular objects, square objects, and pentagons.
Let’s look at some popular 2D game art examples:
Super Mario Bros. (Nintendo)
This iconic 2D game features the character Mario in a side-scrolling platform game. The art style is colorful and cartoonish, with each level having its own unique theme and design. The game’s art has become iconic and is instantly recognizable to gamers worldwide.
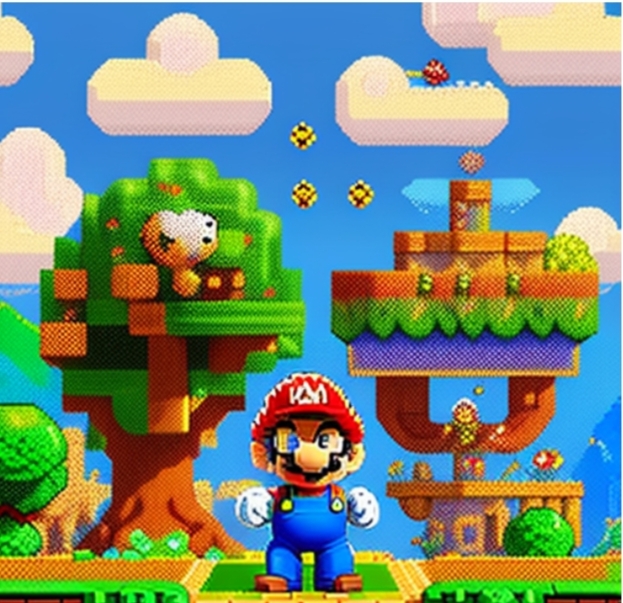

Street Fighter II (Capcom)
This fighting game is known for its detailed 2D character sprites and dynamic backgrounds. Each character has a unique design and set of animations, showcasing the potential of 2D art for character expression.

Cuphead (Studio MDHR)
This recent game is a standout example of 2D art in modern games. The game’s art style is inspired by 1930s cartoons, and each frame of the game was hand-drawn. The game’s unique art style has been widely praised and has won several awards.

3D Game Art
3D, or three-dimensional art, on the other hand, includes length, breadth, and height. This form of art is not flat and has a depth that gives it a sense of volume and space.
3D art is more realistic as it mimics the dimensions of real-world objects. Examples of 3D art include sculptures, installations, and 3D modeling in digital art. Common examples of 3D structures can be a cube, cuboid, prism, pyramid, and cylinder.
Differences between 2D and 3D Game Art structure
While both 2D and 3D art forms are integral parts of visual representation, they have distinct differences.
A 2D structure uses only two axes, the x-axis, and the y-axis, and has only two surfaces; length and breadth.
Conversely, a 3D structure uses three axes, x-axis, y-axis, and z-axis, and has three surfaces; length, breadth, and height.

2D figures, also referred to as “plane” figures or “flat” figures, do not have volume. They exist on flat surfaces and their shape is restricted due to their two-dimensional nature.
Try looking at how shadows are rendered in a 2d game. You can see that it is static
On the other hand, 3D figures have volume and do not appear flat or plane. They can be viewed from different angles, providing a more comprehensive perspective of the object.

Isometric 3d location: Combining 2d and 3d game art
At the crossroads of 2D and 3D art, a unique form of the image appears: Isometric 3D Locations.
This technique combines the simplicity of 2D art with the depth and volume of 3D art to create a unique visual style. Isometric 3D locations are created by projecting a 3D scene onto a 2D landscape in such a way that the three axes of the 3D scene appear to be equally angled. The result is a pseudo-three-dimensional effect that retains the simplicity of 2D art but creates a sense of depth and volume.
This technique is widely used in video games, especially in strategy and role-playing mobile games
Look at the example of locations in game Manor Cafe. These isometric locations were designed by the outsourcing design studio RetroStyle Games.

The use of isometric 3D locations demonstrates the versatility of game art and the creative approach of artists and game designers to combine different forms of visual performance.
Conclusion
Both 2D and 3D art forms have their unique charm and significance. While 2D art is often simpler and more abstract, 3D art offers a more realistic and tangible representation.
Understanding the difference between these two forms of art can help artists and designers make more informed decisions in their creative process, whether they’re creating a traditional painting, a digital illustration, or a 3D model for a video game.
As the world of art continues to evolve and technology advances, the boundaries between 2D and 3D art are becoming increasingly blurred, opening up new possibilities for creative expression.







