Addressing Health Issues in China: Challenges and Opportunities
Introduction:
China, a nation with a rich history and a rapidly growing economy, faces a multitude of health challenges that require urgent attention. With a vast population, environmental concerns, and changing lifestyles, the country is grappling with a range of health issues that have significant implications for its citizens and society as a whole. This article delves into some of the major health challenges faced by China, examines their causes, and explores potential solutions to improve the health and well-being of the nation’s population.
1. Air Pollution and Respiratory Health:
China’s Gimy rapid industrialization and urbanization have led to severe air pollution, particularly in major cities. The toxic mix of industrial emissions, vehicle exhaust, and coal-burning contributes to high levels of fine particulate matter (PM2.5) in the air. Prolonged exposure to such pollution has resulted in respiratory diseases, including asthma, bronchitis, and lung cancer.
To address this issue, the Chinese government has implemented various measures, such as stricter emissions standards, the promotion of clean energy alternatives, and the establishment of pollution control initiatives. Continued efforts to reduce pollution levels and promote sustainable practices are essential to safeguard public health and mitigate the long-term effects of air pollution.
2. Non-communicable Diseases (NCDs):
China is experiencing a significant rise in non-communicable diseases (NCDs), including cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and cancer. Factors contributing to this increase include changing dietary patterns, sedentary lifestyles, and an aging population. These diseases impose a heavy burden on individuals, families, and the healthcare system.
Prevention and early intervention are key strategies to tackle NCDs in China. Raising public awareness about healthy lifestyles, promoting regular physical activity, and implementing policies to regulate the availability and marketing of unhealthy food products are crucial steps toward reducing the prevalence of NCDs. Additionally, strengthening primary healthcare systems and improving access to affordable and quality healthcare services can help effectively manage and treat NCDs.
3. Mental Health Challenges:
Mental health issues have gained recognition as a significant health concern in China. The rapid societal changes, intense academic pressures, and increased urbanization have contributed to rising stress levels, anxiety, depression, and suicide rates, particularly among the younger population.
To address mental health challenges, China has made efforts to improve mental health services and increase awareness. Initiatives include the establishment of mental health hotlines, the integration of mental health education in schools, and the expansion of mental health services in primary healthcare settings. However, there is a need for further investment in mental health infrastructure, DE stigmatization of mental illness, and the provision of accessible and affordable mental health services throughout the country.
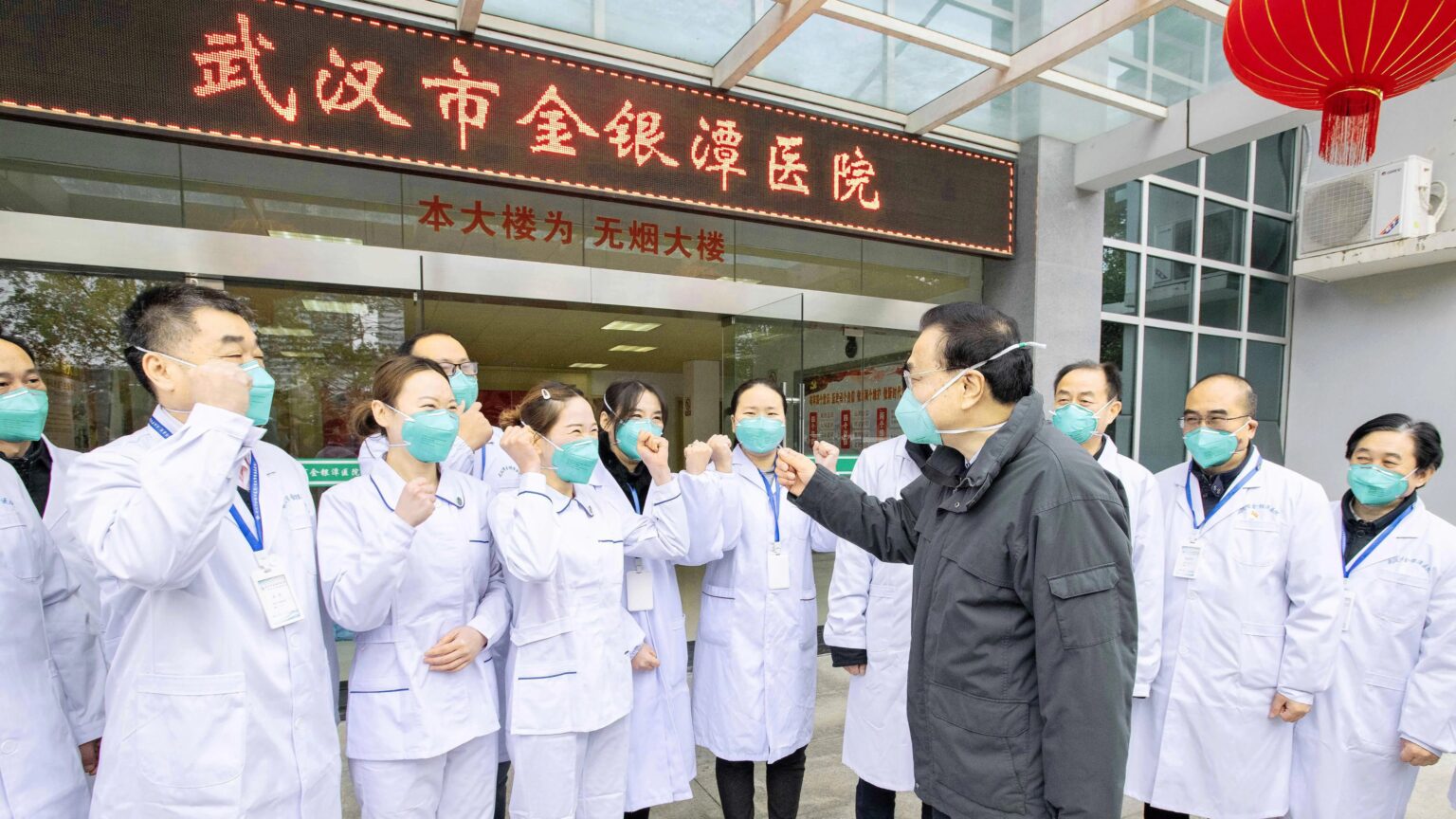
4. Infectious Diseases and Public Health Preparedness:
China has experienced several outbreaks of infectious diseases in recent years, including the severe acute respiratory syndrome ( 中國人線上看 ) in 2003, the H1N1 influenza pandemic in 2009, and the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic. These outbreaks have highlighted the importance of robust public health systems and preparedness in responding to infectious diseases.
China has taken significant steps to strengthen its public health infrastructure, including the establishment of the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention (China CDC) and the improvement of disease surveillance and response mechanisms. Continued investment in public health systems, early detection and containment of infectious diseases, and international collaboration are vital to effectively manage future outbreaks and protect public health.
5. Healthcare Access and Disparities:
Ensuring equitable access to healthcare remains a challenge in China, particularly in rural areas and among marginalized populations. The country has made substantial progress in expanding healthcare coverage through the implementation of the Universal Health Coverage (UHC) system. However, regional disparities in healthcare resources, affordability, and quality of care persist
To bridge the healthcare access gap, China must focus on improving healthcare infrastructure in rural areas, recruiting and retaining healthcare professionals in underserved regions, and reducing financial barriers to healthcare services. Enhancing primary healthcare delivery, promoting health insurance schemes, and implementing targeted interventions for vulnerable populations are crucial steps toward achieving equitable access to healthcare.
Conclusion:
China’s health challenges are complex and multifaceted, requiring comprehensive and coordinated efforts from various stakeholders. By addressing issues such as air pollution, non-communicable diseases, mental health, infectious diseases, and healthcare access disparities, China can pave the way for a healthier future. The Chinese government, healthcare providers, communities, and individuals must work together to implement effective policies, strengthen public health systems, promote health education, and prioritize preventive measures. By doing so, China can overcome its health challenges and build a robust and resilient healthcare system for the well-being of its population.